Turbulence in blood
Transient turbulence in a Fontan patient's circulation.
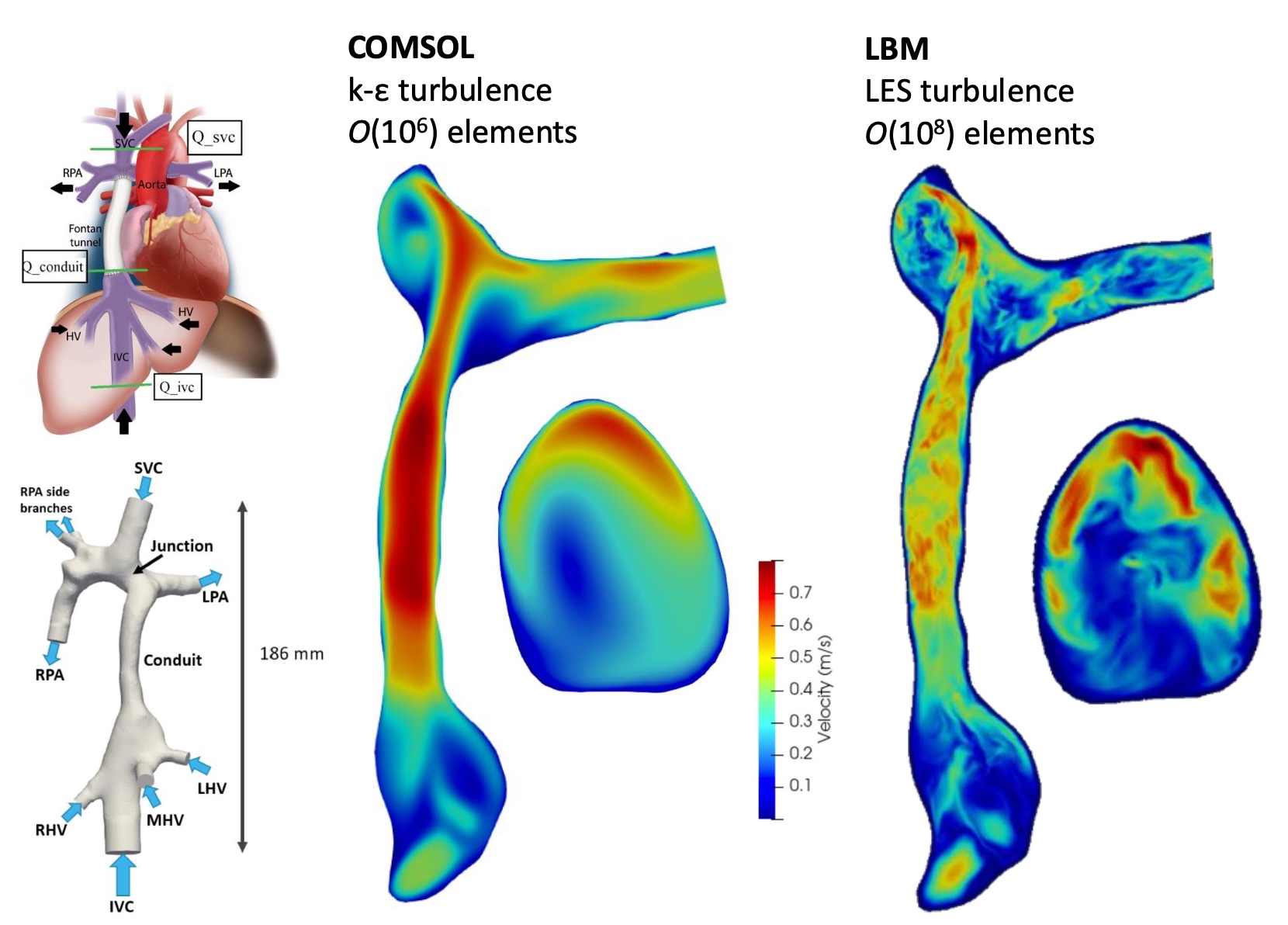
Fontan procedure is a surgery strategy to help patients with congenital heart disease (CHD) by creating artificial connection between the veins and pulmonary artery. Fontan patients often suffer from diminished quality of life due to impaired hemodynamics in Fontan physiology and the associated risk of thrombosis. Patient-specific computational fluid dynamics (CFD) simulations are extensively utilized for analyzing blood flow patterns in Fontan, aiding clinical decision-making. However, existing research relies on turbulence models to resolve blood flow turbulence, resulting in the loss of small-scale information within the flow field. Studies demonstrating the relevance of these small-scale information from macroscopic hemodynamic parameters are currently lacking. This study aims to fill this research gap. The distinctive contribution of this study is conducting direct numerical simulation (DNS) based on the Lattice Boltzmann method (LBM) with extremely high resolution in a patient-specific total cavopulmonary connection (TCPC) and comparing a select set of hemodynamic metrics with the outcomes of large eddy simulation (LES). The investigated metrics include wall shear stress (WSS), wall shear rate (WSR), elongation rate (ER) and flowtype parameters. The study’s findings reveal noteworthy disparities in these metrics between DNS and LES. This discrepancy suggests that LES tends to overestimate the low WSS zone and underestimate the elongation dominated zone. These metrics serve as indicators of thrombosis, thus potentially indicating an overestimation of coagulation cascade and an underestimation of platelet adhesion caused by Von Willebrand factor (vWF) uncoiling. Furthermore, this study quantitatively proposes that there exists significant elongation dominated flow field in TCPC for the first time. Considering the high fidelity of DNS, this study can serve as a benchmark for future Fontan hemodynamic investigations.
Related MSc theses:
M Blom - Quantifying non-stationary inhomogeneous turbulence in flow fields